
Creating a WordPress theme can be a rewarding experience. You get ultimate control of your website built on the wordpress platform if you know a little coding. This is a step by step guide to help you get started on your new theme.
Set Up Your Development Environment
– Local Development Tool: Use a local development environment like Local by Flywheel, XAMPP, or MAMP to run WordPress on your computer.
– Text Editor: Use a code editor like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, or Atom for writing your theme files.
Create the Theme Folder
– Inside the wp-content/themes/ directory of your WordPress installation, create a new folder for your theme. Name it something like my-custom-theme.
Add the Required Theme Files
– style.css: This file is essential for WordPress to recognize your theme. It contains metadata about your theme.
CSS
/*
Theme Name: My Custom Theme
Theme URI: https://example.com/my-custom-theme
Author: Your Name
Author URI: https://example.com
Description: A custom WordPress theme.
Version: 1.0
Text Domain: my-custom-theme
*
– index.php: This is the main template file that WordPress uses to display content.
<?php get_header(); ?>
<div id="primary" class="content-area">
<main id="main" class="site-main">
<?php
if (have_posts()) :
while (have_posts()) : the_post();
get_template_part('template-parts/content', get_post_type());
endwhile;
else :
get_template_part('template-parts/content', 'none');
endif;
?>
</main>
</div>
<?php get_sidebar(); ?>
<?php get_footer(); ?>
– functions.php: This file allows you to add custom functions and hooks to your theme
<?php
function my_custom_theme_setup() {
add_theme_support('title-tag');
add_theme_support('post-thumbnails');
register_nav_menus(array(
'primary' => __('Primary Menu', 'my-custom-theme'),
));
}
add_action('after_setup_theme', 'my_custom_theme_setup');
function my_custom_theme_scripts() {
wp_enqueue_style('my-custom-theme-style', get_stylesheet_uri());
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'my_custom_theme_scripts');
– header.php: This file contains the HTML structure for the header section.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html <?php language_attributes(); ?>>
<head>
<meta charset="<?php bloginfo('charset'); ?>">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title><?php wp_title(); ?></title>
<?php wp_head(); ?>
</head>
<body <?php body_class(); ?>>
<header id="masthead" class="site-header">
<div class="site-branding">
<h1 class="site-title"><a href="<?php echo esc_url(home_url('/')); ?>" rel="home"><?php bloginfo('name'); ?></a></h1>
<p class="site-description"><?php bloginfo('description'); ?></p>
</div>
<nav id="site-navigation" class="main-navigation">
<?php
wp_nav_menu(array(
'theme_location' => 'primary',
'menu_id' => 'primary-menu',
));
?>
</nav>
</header>
– footer.php: This file contains the HTML structure for the footer section.
<footer id="colophon" class="site-footer">
<div class="site-info">
<a href="<?php echo esc_url(__('https://wordpress.org/', 'my-custom-theme')); ?>">
<?php
printf(esc_html__('Proudly powered by %s', 'my-custom-theme'), 'WordPress');
?>
</a>
</div>
</footer>
<?php wp_footer(); ?>
</body>
</html>
– sidebar.php: This file contains the HTML structure for the sidebar.
<aside id="secondary" class="widget-area">
<?php dynamic_sidebar('sidebar-1'); ?>
</aside>
Add Custom Templates (Optional)
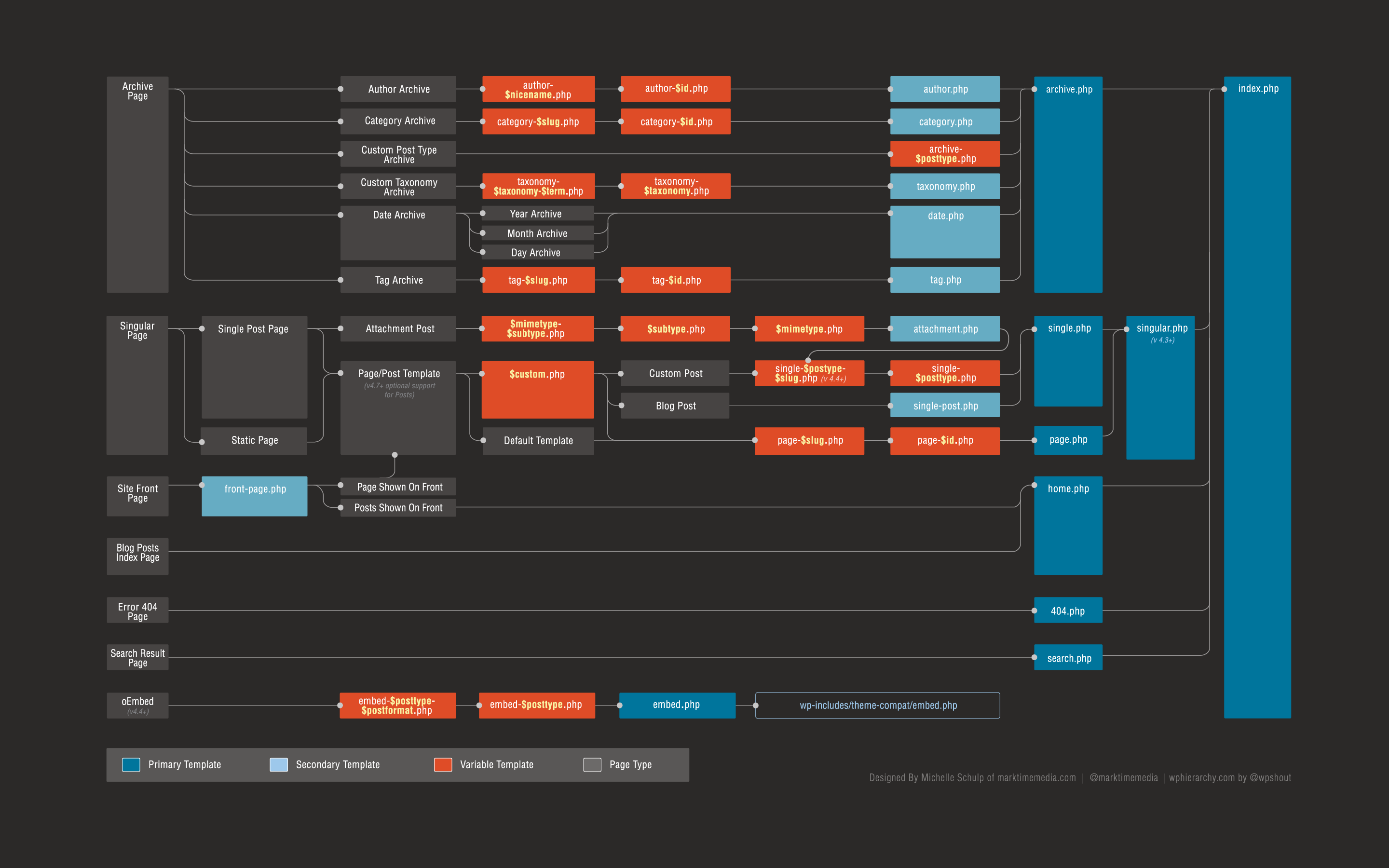
– front-page.php: If you want a custom front page, create this file.
– page.php: Custom template for pages.
– single.php: Custom template for single posts.
– archive.php: Custom template for archives.
Enqueue Styles and Scripts
– In functions.php, you can enqueue additional CSS and JavaScript files.
function my_custom_theme_scripts() {
wp_enqueue_style('my-custom-theme-style', get_stylesheet_uri());
wp_enqueue_script('my-custom-theme-script', get_template_directory_uri() . '/js/script.js', array(), '1.0', true);
}
add_action('wp_enqueue_scripts', 'my_custom_theme_scripts');
Activate Your Theme
– Go to the WordPress admin dashboard, navigate to Appearance > Themes, and activate your new theme.
Customize Your Theme
– Use Customizer to add custom styles, colors, and other settings.
– Create custom Widgets and Menus.
– Add Custom Post Types and Taxonomies if needed.
Test Your Theme
– Test your theme on different devices and browsers to ensure compatibility.
– Check for any errors or warnings in the WordPress debug log.
Deploy Your Theme
– Once you’re satisfied with your theme, you can deploy it to your live WordPress site.
– Consider using version control (e.g., Git) to manage your theme files.
Documentation and Support
– Document your theme for future reference.
– Provide support for users who might use your theme.
Additional Tips
Use a Starter Theme:
- Consider using a starter theme like Underscores or Genesis to speed up development. These themes provide a solid foundation with minimal styling, allowing you to focus on customization.
Leverage Child Themes:
- If you’re customizing an existing theme, create a child theme instead of modifying the parent theme directly. This allows you to update the parent theme without losing your customizations.
Optimize for Performance:
- Minimize CSS and JavaScript files.
- Use lazy loading for images.
- Leverage browser caching and CDN for faster load times.
Accessibility:
- Ensure your theme is accessible by following best practices for keyboard navigation, screen reader compatibility, and semantic HTML.
SEO Optimization:
- Use proper heading structures (
<h1>,<h2>, etc.). - Ensure your theme supports meta tags and Open Graph tags.
- Use clean, descriptive URLs.
Additional Resources
WordPress Theme Handbook:
- WordPress Theme Handbook
- Comprehensive guide on WordPress theme development, including best practices, templates, and functions.
Theme Unit Test:
- Theme Unit Test
- A dataset you can import into your WordPress site to test your theme’s compatibility with various content types and layouts.
WP Rig:
- WP Rig
- A modern WordPress development rig that includes build tools, linting, and optimization features.
Theme Sniffer Plugin:
- Theme Sniffer
- A plugin that checks your theme against WordPress coding standards and best practices.
CSS-Tricks:
- CSS-Tricks
- A great resource for learning CSS, JavaScript, and other web development topics.
Mozilla Developer Network (MDN):
- MDN Web Docs
- Comprehensive documentation on HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and web APIs.







Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.