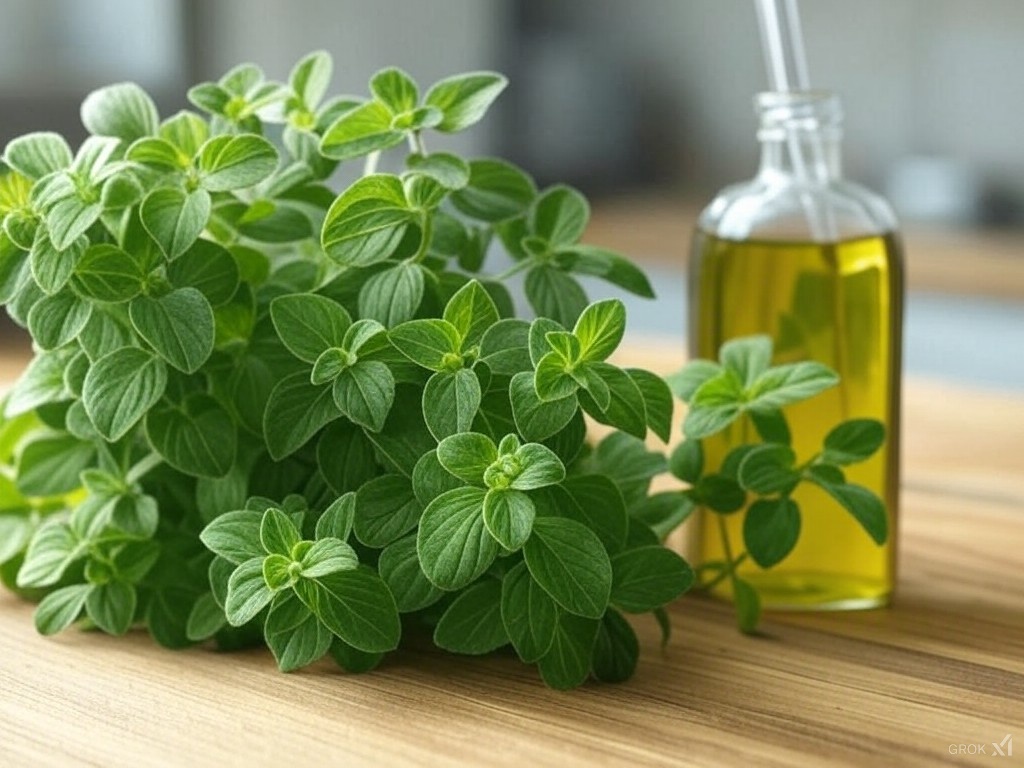
Oregano (Origanum vulgare) is a versatile herb with both culinary and medicinal uses, valued for its rich nutrient profile and bioactive compounds. Here’s a structured overview of its benefits, healing properties, and components:
Oregano vs Amoxicillin school experiment
Nutritional Profile
Oregano is rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, including:
- Vitamins: K (essential for blood clotting), A (supports vision/immunity), C (antioxidant), E (skin health), and B vitamins.
- Minerals: Calcium, iron (blood health), magnesium, potassium, and manganese.
- Fiber: Aids digestion.
While typically consumed in small amounts as a herb, its nutrient density contributes to overall health.
Key Bioactive Compounds
- Carvacrol: A phenol with antimicrobial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Thymol: Similar to carvacrol, effective against pathogens and supports immune function.
- Rosmarinic Acid: Potent antioxidant that reduces oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin, luteolin): Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Health Benefits & Healing Properties
Antimicrobial Activity:
- Effective against bacteria (e.g., E. coli, Salmonella), fungi (e.g., Candida), and parasites. Oregano oil may even combat antibiotic-resistant strains.
- Used traditionally for wound disinfection and food preservation.
Antioxidant Effects:
- Neutralizes free radicals, reducing oxidative stress linked to chronic diseases (e.g., heart disease, diabetes).
Anti-Inflammatory Properties:
- May alleviate conditions like arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease by inhibiting inflammatory enzymes.
Respiratory Health:
- Used in folk medicine to relieve coughs, colds, and bronchitis. Inhalation of oregano oil may ease congestion.
Digestive Support:
- Stimulates bile flow, aiding digestion. May combat gut infections and bloating.
Immune Boost:
- Compounds like thymol and carvacrol enhance immune response, potentially reducing infection severity.
Potential Anticancer Properties:
- Preliminary studies suggest carvacrol and rosmarinic acid may inhibit cancer cell growth, though human trials are needed.
Skin Health:
- Oregano oil’s antimicrobial properties can help treat acne or minor wounds when diluted and applied topically.
Forms & Usage
- Culinary: Fresh or dried leaves in cooking (e.g., sauces, marinades).
- Essential Oil: Concentrated form used in aromatherapy or topical applications (always dilute with a carrier oil).
- Supplements: Capsules or tinctures for targeted benefits.
Safety Considerations
- Culinary Use: Safe in typical food amounts.
- Supplements/Oil: High doses may cause gastrointestinal upset or interact with medications (e.g., blood thinners). Consult a healthcare provider before use.
- Pregnancy: Avoid medicinal doses, as oregano oil may stimulate uterine contractions.
Conclusion
Oregano offers a blend of nutrients and potent bioactive compounds, supporting immune function, digestion, and inflammation reduction. While its traditional uses are broad, scientific evidence supports its antimicrobial and antioxidant effects most strongly. Oregano oil, in particular, should be used cautiously due to its potency. Always prioritize evidence-based applications and consult a professional for therapeutic use.